Sending a message with xCall
In the following document we are going to go in detail about the process of sending a cross chain encoded message using xCall.
The following example uses a program written in JavaScript (nodejs) and the repository for it can be found in the following link:
We are going to interact with 2 JVM chains, the origin chain being the Lisbon testnet on ICON and the destination chain the Altair testnet on Havah. We are going to send a hex encoded string as a message from the origin chain and go through the lifecycle of a cross-chain message with xCall.
Prerequisites
As a prerequisite to follow this tutorial you have to setup the following.
- Clone the repo for the demo (https://github.com/icon-project/xcall-multi-jvm-jvm-demo (opens in a new tab)).
- Have ICX testnet balance for the Lisbon chain, you can use the following faucet (opens in a new tab).
- Have HVH testnet balance for the Altair chain (use the following faucet (opens in a new tab)).
Before diving into the process of using xCall to send messages across blockchains is important to notice that due to the nature of this process a moderate level of knowledge about programming with JavaScript and interacting with blockchains is necessary to be able to follow the explanation.
In this document we are going to be doing the following task:
- Signing transactions on the ICON Network and on EVM Chains.
- Making readonly calls to ICON Network and EVM Chains.
- Utilize special SDK and libraries designed for blockchains (icon-js-sdk, hardhat, ethers.js, web3js).
Because of this is highly recommended that you are already familiar with these task in order to fully understand the process that is going to be explained.
Smart contract on the destination chain
Using xCall is an straightforward process, you send message from a source chain by calling the sendCallMessage method of the xCall contract and you receive that message on the destination chain, but in order to properly receive that message is necessary to have a smart contract implemented in the destination chain with a method named handleCallMessage.
/**
* Handles the call message received from the source chain.
* Only called from the Call Message Service.
*
* @param _from The network address of the caller on the source chain
* @param _data The calldata delivered from the caller
* @param _protocols The contract addresses that delivered the data, if omitted the default protocol was used
*/
external handleCallMessage(String _from, byte[] _data);
external handleCallMessage(String _from, byte[] _data, @Optional String[] _protocols);The handleCallMessage method of your smart contract in the destination chain will be the receiver of the message that you are going to be sending from the source chain.
For the purpose of this explanation, a contract as already being deployed on both chains (Lisbon and Altair). You can find the addresses of the smart contract on the config file of the demo (opens in a new tab).
Sending a message
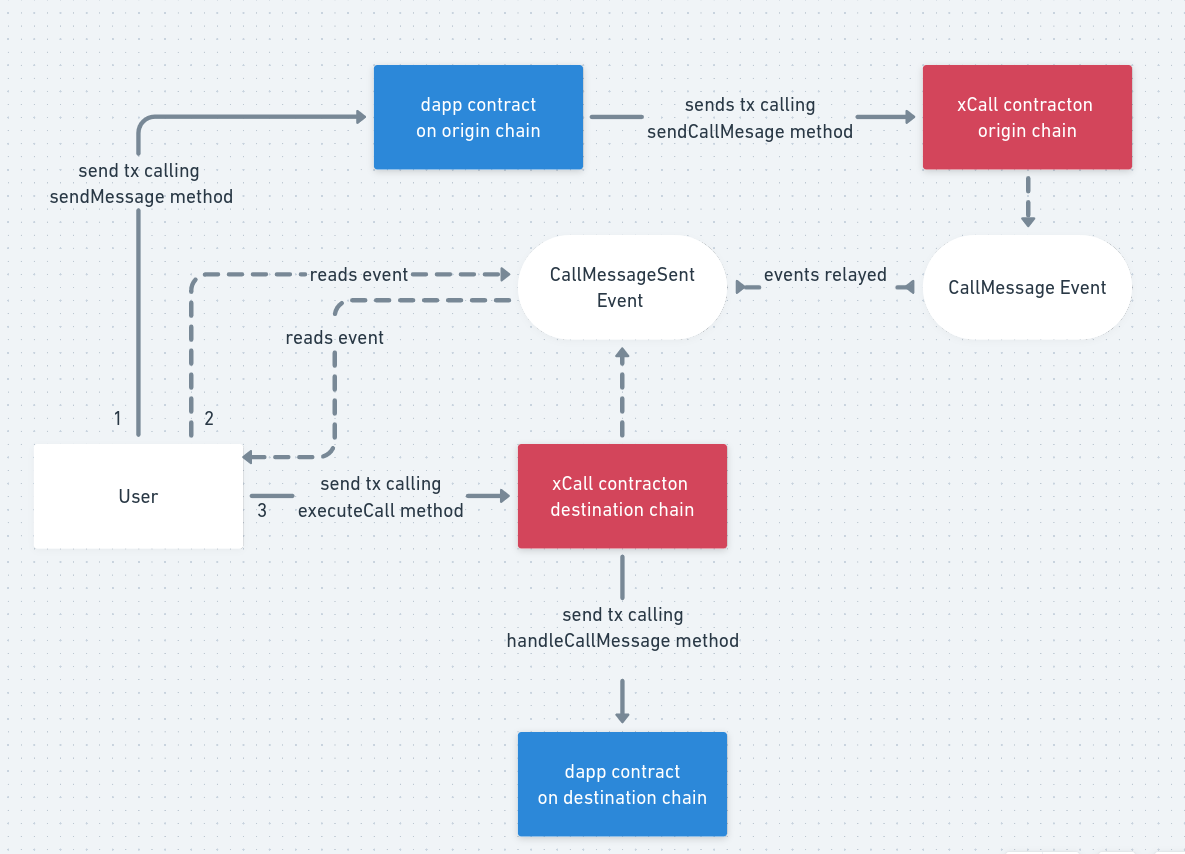
To send a message using xCall you sign a transaction calling the sendCallMessage method of the xCall contract on the source chain.
/**
* Sends a call message to the contract on the destination chain.
*
* @param _to The network address of the callee on the destination chain
* @param _data The calldata specific to the target contract. Max 2048KB
* @param _rollback (Optional) Data used to specify error handling of a two-way messages. Max 1024KB
* @param _sources (Optional) The contracts that will be used to send the message
* @param _destinations (Optional) The addresses of the contracts that xcall will expect the message from.
*
* @return The serial number of the request
*/
payable external sendCallMessage(String _to,
byte[] _data,
@Optional bytes _rollback,
@Optional String[] _sources
@Optional String[] _destinations) return Integer;When the xcall contract on the source chain receives the call request message, it sends the _data to the network address (opens in a new tab) _to on the destination chain.
- The
_dataparam is an arbitrary payload, the xCall interface doesn't care about what you are sending, it leaves the encoding and decoding of this data to the Dapp that you are developing, for example it can be a hex encoded string, or a hex encoded number, etc. - The
_toparam is a network address (opens in a new tab) of the callee contract which receives the_datapayload on the destination chain. - The
_rollbackparameter is for handling error cases. If the_rollbackparameter is not null, then the source chain will receive a response message back regardless of whether the destination chain execution of the message request fails. For more information, see Error Handling (opens in a new tab).
Using the icon-sdk-js we can send the signed transaction invoking the sendCallMessage method of the xcall contract as shown in the following code.
// IMPORTS
require("dotenv").config();
const IconService = require("icon-sdk-js");
const { ethers } = require("ethers");
const { BigNumber } = ethers;
const Web3Utils = require("web3-utils");
const fs = require("fs");
// CONSTANTS
// CHANGE THESE VALUES TO YOUR OWN
const ICON_WALLET_PK = process.env.PK_ICON; // private key of your Lisbon wallet
const HAVAH_WALLET_PK = process.env.PK_HAVAH; // private key of your Altair wallet
const ICON_XCALL_ADDRESS = "cx15a339fa60bd86225050b22ea8cd4a9d7cd8bb83";
const HAVAH_XCALL_ADDRESS = "cxf35c6158382096ea8cf7c54ee338ddfcaf2869a3";
const HAVAH_DAPP_ADDRESS = "cx8575a4f97bb89c284d4a734e4926884d90c22871"
const HAVAH_CHAIN_LABEL = "0x111.icon";
const ICON_CHAIN_LABEL = "0x2.icon";
// SETTINGS
const {
IconWallet,
IconBuilder,
SignedTransaction,
IconConverter,
HttpProvider
} = IconService.default;
const { CallTransactionBuilder } = IconBuilder;
const ICON_RPC_URL = "https://lisbon.net.solidwallet.io/api/v3";
const ICON_RPC_NID = 2;
const EVM_RPC_URL = "https://ctz.altair.havah.io/api/v3/icon_dex";
const HAVAH_RPC_NID = 273;
const ICON_HTTP_PROVIDER = new HttpProvider(ICON_RPC_URL);
const ICON_SERVICE = new IconService.default(ICON_HTTP_PROVIDER);
const HAVAH_HTTP_PROVIDER = new HttpProvider(HAVAH_RPC_URL);
const HAVAH_SERVICE = new IconService.default(HAVAH_HTTP_PROVIDER);
const ICON_SIGNER = IconWallet.loadPrivateKey(ICON_WALLET_PK);
const HAVAH_SIGNER = IconWallet.loadPrivateKey(HAVAH_WALLET_PK);
// ICON CHAIN FUNCTIONS
async function sendCallMessage(to, data) {
try {
const wallet = ICON_SIGNER;
const txObj = new CallTransactionBuilder()
.from(wallet.getAddress())
.to(ICON_XCALL_ADDRESS)
.stepLimit(IconConverter.toBigNumber(2000000))
.nid(IconConverter.toBigNumber(ICON_RPC_NID))
.nonce(IconConverter.toBigNumber(1))
.version(IconConverter.toBigNumber(3))
.timestamp(new Date().getTime() * 1000)
.method("sendCallMessage")
.params({
_to: to,
_data: data
})
.build();
console.log("# sendCallMessage tx object:");
console.log(txObj);
const signedTransaction = new SignedTransaction(txObj, wallet);
return await ICON_SERVICE.sendTransaction(signedTransaction).execute();
} catch (e) {
console.log("Error running sendCallMessage");
throw new Error(e);
}
}
// UTILITY FUNCTIONS
function getNetworkAddress(network, address) {
return `${network}/${address}`;
}
async function sleep(time) {
await new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, time);
});
}
function encodeMessage(msg) {
const encoded = Web3Utils.fromUtf8(msg);
return encoded;
}
function decodeMessage(msg) {
const decoded = Web3Utils.hexToString(msg);
return decoded;
}
// MAIN LOGIC
async function main() {
try {
// Encode the message to send
const dataToSend = encodeMessage("Hello from ICON");
console.log("\n## Encoded message:", dataToSend);
// Get the dapp contract network address on the destination chain
const networkAddressDestination = getNetworkAddress(
HAVAH_CHAIN_LABEL,
HAVAH_DAPP_ADDRESS
);
const networkAddressSource = getNetworkAddress(
ICON_CHAIN_LABEL,
ICON_SIGNER.getAddress()
);
// send the call message to the destination chain
const callMessageTxHash = await sendCallMessage(
networkAddressDestination,
dataToSend
);
console.log("\n## Call message tx hash:", callMessageTxHash);
} catch (e) {
console.log("error running main function:", e);
}
}
main();
This method returns the serial number of the request. The serial number is the unique identifier of the message request on the source chain.
This method is payable, and dApps need to call this method with proper fees. dApps that want to make a call to sendCallMessage can query the total fee amount for the destination network via the getFee method, and then enclose the appropriate fees in the method call. For more information on fees, see Fees Handling (opens in a new tab).
/**
* Gets the fee for delivering a message to the _net.
* If the sender is going to provide rollback data, the _rollback param should set as true.
* The returned fee is the total fee required to send the message.
*
* @param _protocol The protocol/connection used
* @param _net The network id
* @param _rollback Indicates whether it provides rollback data
* @param _sources The protocols used to send the message is omitted default protocol is used.
* @return The total fee of sending the message
*/
external readonly getFee(String _net,
boolean _rollback
@Optional String[] _sources) returns Integer;/**
* Gets the protocol fee for sending a xCall message
*
* @return the xCall protocol fee
*/
external readonly getProtocolFee() Returns Integer;The _net parameter is the network address (opens in a new tab) of the destination chain to query the fee for sending a message to.
Fetching event in source chain
After sending the message you have to now listen to the CallMessageSent event on the source chain.
/**
* Notifies that the requested call message has been sent
* @param _from the network address of the caller
* @param _to the network address of the callee
* @param _sn the serial number of the request
*/
@EventLog(indexed=3) void CallMessageSent(Address _from,
String _to,
Integer _sn);To listen to this event you have to make consecutive RPC queries with the icx_getTransactionResult method using the hash of the transaction for the sendCallMessage call.
async function getTransactionResultICON(txHash) {
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
const txResult = await ICON_SERVICE.getTransactionResult(
txHash
).execute();
return txResult;
} catch (e) {
console.log(`txResult (pass ${i}):`, e);
}
await sleep(1000);
}
}The call will respond with an error status of Pending or Executing until the transaction have been processed by the network and then you will have an object response like the following:
{
"status": 1,
"to": "cx17cb94775d2f774277bfbf3477be5f36ca5af37f",
"txHash": "0xd2c19a61af825474960e9a5b22e38e90533280924d22ea49bcd191be6f7dd469",
"txIndex": 1,
"blockHeight": 394373,
"blockHash": "0xb96c59c8f8763ce599030d2f6c9d0b96b17205c596a65cb0044b9330de3c7299",
"cumulativeStepUsed": "1211098",
"stepUsed": "1211098",
"stepPrice": "12500000000",
"eventLogs": [
{
"scoreAddress": "cx0000000000000000000000000000000000000000",
"indexed": ["BTPMessage(int,int)", "0x2", "0x97"],
"data": []
},
{
"scoreAddress": "cx1b8e75486efec00680c62c57e744fd683f5b2858",
"indexed": ["BTPEvent(str,int,str,str)", "0x3.icon", "0x8d"],
"data": ["0x539.hardhat", "SEND"]
},
{
"scoreAddress": "cx17cb94775d2f774277bfbf3477be5f36ca5af37f",
"indexed": [
"CallMessageSent(Address,str,int,int)",
"hxb6b5791be0b5ef67063b3c10b840fb81514db2fd",
"btp://0x539.hardhat/0x959922bE3CAee4b8Cd9a407cc3ac1C251C2007B1",
"0x8c"
],
"data": ["0x8d"]
}
],
"logsBloom": "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000200001000008200400000810000000480000000000000000000000000000002000004000000000000000000020000000000000000000000000802000000000082800000a000000000000000000000000000000000000000800000000000008000000000000000000000000000000400000000400000008000100000400000020000000000000000000080140000000000000000000000000000000400000000000000000000000000000000000000002002010000840200000000400000000000100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000"
}Fetching event on destination chain
The CallMessage event on the destination chain can be fetched to verify that the xcall interface on the destination chain has a new message that needs to be executed.
/**
* Notifies that the a new message is received by xCall and
* is ready to be executed.
* @param _from the network address of the caller
* @param _to A string representation of the callee address
* @param _sn the serial number of the request
* @param _reqId the request ID of the destination chain used in execute call
* @param _data the calldata
*/
@EventLog(indexed=3) void CallMessage(String_from,
String _to,
Integer _sn,
Integer _reqId,
byte[] _data);Similar as the process of listening to the CallMessageSent event on the origin chain, we now wait for the CallMessage event on the destination chain.
Since we dont know the exact moment the event will be raised we need to listen block by block to the destination chain for the event.
The demo dapp implements a simple block monitor that you can use to fetch the CallMessage event (and the rest of the events related to a cross chain message sent with xCall).
- block monitor (https://github.com/icon-project/xcall-multi-jvm-jvm-demo/blob/master/utils/monitor.js (opens in a new tab))
This event will give us the _reqId param that is necessary for us to use as a param in the next step to process and make the xCall contract send that message to our DApp smart contract on the destination chain.
Execute call on destination chain
Once you have verified that the event has been raised in the destination chain, you have to now sign a transaction to trigger the process that will allow the xCall contract to send the message to your smart contract with the handleCallMessage method.
This transaction is being done by calling the executeCall method in the xCall contract on the destination chain:
/**
* Executes the requested call message.
* @param _reqId the request ID of the destination chain
* @param _data the calldata
*/
external executeCall(BigInteger _reqId, byte[] _data);The _reqId is the unique identifier of the message request on the destination chain, we get this value in the callMessage event on the destination chain (the previous step).
async function executeCall(reqId, data) {
try {
const wallet = HAVAH_SIGNER;
const txObj = new CallTransactionBuilder()
.from(wallet.getAddress())
.to(HAVAV_XCALL_ADDRESS)
.stepLimit(IconConverter.toBigNumber(2000000))
.nid(IconConverter.toBigNumber(HAVAH_RPC_NID))
.nonce(IconConverter.toBigNumber(1))
.version(IconConverter.toBigNumber(3))
.timestamp(new Date().getTime() * 1000)
.method("executeCall")
.params({
_reqId: reqId,
_data: data
})
.build();
console.log("# executeCall tx object:");
console.log(txObj);
const signedTransaction = new SignedTransaction(txObj, wallet);
return await HAVAH_SERVICE.sendTransaction(signedTransaction).execute();
} catch (e) {
console.log("Error running executeCall");
throw new Error(e);
}
}Like previously stated the DApp on the destination chain must implement handleCallMessage. When the user calls the executeCall method, the xcall contract invokes the following predefined method in the target DApp with the call data associated in the CallMessage _reqId.
Fetching event on destination chain after executeCall
To notify the execution result of DApp handleCallMessage method, the following event is emitted after its execution.
/**
* Notifies that the message was executed
* @param _reqId the request ID of the message
* @param _code the execution result code (1: Success, 0: Failure)
* @param _msg Error message
*/
@EventLog(indexed=1) void CallExecuted(Integer _reqId,
Integer _code,
String _msg)Verify received message (Optional)
For this DApp a MessageReceived event method has been implemented to verify the message has been received, this is not a requirement but is a recommended step.
/**
* Verifies the message has been received
* @param _from message sender
* @param _data encoded message
*/
@EventLog void MessageReceived(String_from, byte[] _data)Decode message sent (Optional)
The _data param of the result in the previous step is a hex encoded string, once you decode it we can now see the string message that we originally sent from ICON:
## Decoded message sent via xcall
Hello this is xCall live!References
- xCall Standard: github repo (opens in a new tab)
- IBC on ICON: https://github.com/icon-project/IBC-Integration (opens in a new tab)